You can get far in biology by asking: “Which came first, the chicken or the egg?†Max Cooper discovered the basis of modern immunology by asking basic questions.
Cooper was selected for the 2012 Dean’s Distinguished Faculty Lecture and Award, and on Thursday evening dazzled an Emory University School of Medicine audience with a tour of his scientific career. He joined the Emory faculty in 2008 as a Georgia Research Alliance Eminent Scholar.

Max Cooper, MD
Cooper’s research on the development of the immune system, much of it undertaken before the era of cloned genes, formed the underpinnings of medical advances ranging from bone marrow transplants to monoclonal antibodies. More recently, his research on lampreys’ divergent immune systems has broadened our picture of how adaptive immunity evolved.
Cooper grew up in Mississippi and was originally trained as a pediatrician, and became interested in inherited disorders that disabled the immune system, leaving children vulnerable to infection. He joined Robert Good’s laboratory at the University of Minnesota, where he began research on immune system development in chickens.
In the early 1960s, Cooper explained, scientists thought that all immune cells developed in one place: the thymus. Working with Good, he showed that there are two lineages of immune cells in chickens: some that develop in the thymus (T cells) and other cells responsible for antibody production, which develop in the bursa of Fabricius (B cells). [On Thursday, he evoked chuckles by noting that a critical discovery that drove his work was published in the journal Poultry Science after being rejected by Science.]
Cooper moved on to the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and there made several discoveries related to how B cells develop. A collaboration with scientists at University College, London led to the identification of the places where B cells develop in mammals: fetal liver and adult bone marrow.
Cooper’s research on lampreys began in Alabama and has continued after he came to Emory in 2008. Primitive lampreys are thought to be an early offshoot on the evolutionary tree, before sharks, the first place where an immune system resembling those of mammals and birds is seen. Lampreys’ immune cells produce “variable lymphocyte receptors†that act like our antibodies, but the molecules look very different in structure. These molecules were eventually crystallized and their structure probed, in collaboration with Ian Wilson in San Diego.
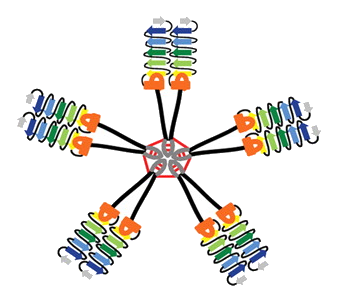
Lampreys have variable lymphocyte receptors, which resemble our antibodies in function but not in structure
Cooper said he set out to figure out “which came first, T cells or B cells?†but ended up discovering something even more profound. He found that lampreys also have two separate types of immune cells, and the finding suggests that the two-arm nature of the immune system may have preceded the appearance of the particular features that mark those cells in evolution.




